
Thymeleaf使用
发布于2021-06-12 13:47 阅读(1010) 评论(0) 点赞(9) 收藏(0)
本文只适用于不会Java对HTML语言有基础的程序员们,是浏览了各大博客后收集整理,重新编辑的一篇文章,希望能对大家有所帮助。最后本文如果有哪里写错的,希望各位大神们能够批评指正,谢谢大家!
对于Thymeleaf,网上特别官方的解释无非就是:网站或者独立应用程序的新式的服务端java模板引擎,可以执行HTML,XML,JavaScript,CSS甚至纯文本模板。这个解释没有任何问题,它确实是建立在Java的基础之上的,但是像我这种只会前端不懂Java的人,其实也可以运用它。了解angular的人在看到Thymeleaf就会感到惊喜,它们在形式上其实是比较相似的。那么,Thymeleaf需要从那里看起?作为Java小白,刚开始看了网上那么多Thymeleaf文章也看不出个所以然,今天好不容易才整理出头绪,接下来就开始切入正题:
<td th:text="${food.name}">noodles</td>如上图,后台传出的food.name会将静态数据“noodles”替换掉,若访问静态页面,则显示数据“noodles”。是不是和angular很像?下面我们就来换一种方式,不同于其他博客上的方式来介绍Thymeleaf。
当然,首先大家要先知道th简单表达式:
一、th简单表达式:
① ${...} 变量表达式:
<input type="text" name="userName" value="Beyrl" th:value="${user.name}" />上述代码为引用user对象的name属性值。
② *{...} 选择表达式:
- <div th:object="${session.user}">
-
- <p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">XXXX</span>.</p>
-
- </div>
选择表达式一般跟在th:object后,直接选择object中的属性。
③ #{...} 消息文字表达式:
<p th:utext="#{home.welcome}">Welcome to our grocery store!</p>④ @{...} 链接url表达式:
<a href="details.html" th:href="@{/webPage/details(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a>@{……}支持决定路径和相对路径。其中相对路径又支持跨上下文调用url和协议的引用(//code.jquery.com/jquery-2.0.3.min.js)。
当URL为后台传出的参数时,代码如下:
<img src="../../webPage/food/images/pizza.jpg" th:src="@{${path}}" alt="披萨" />当理解了这四个表达式后,我就信心满满的去向下看文档,然后我发现我看不懂了。。。因为我不理解什么是th:field='';th:action='';诸如此类的好多好多,后来在一个博客上看到这一类的是所谓的Thymeleaf的属性,或者是常用的th:标签,下面我们就来整理学习一下这些标签:
这是在一个博客上看到的整理的较全的图片,还有一个更全的,那个太多了,会吓到初学者,不知道你们会不会,反正我是被吓到了。。。
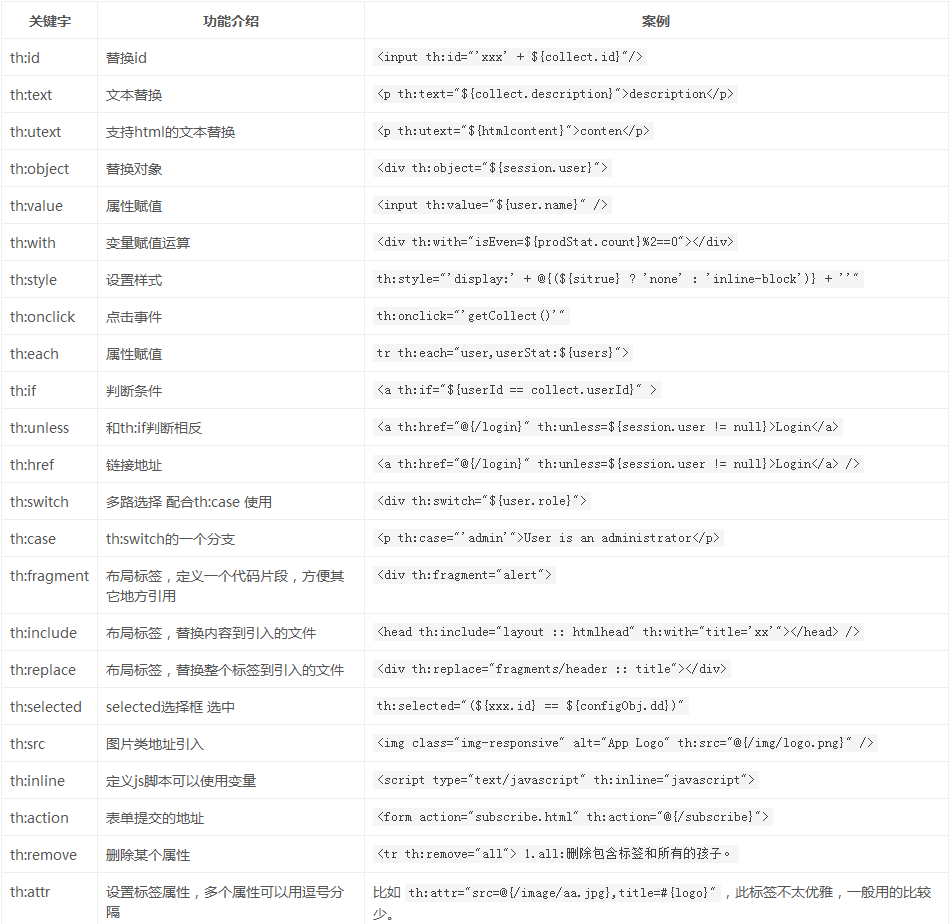
下面我们会详细介绍一些常用的标签:
二、th常用标签:
1.th:id:
类似html标签中的id属性。
<div class="student" th:id = "food+(${pizza.index}+1)"></div>2.th:text:与th:utext:
即文本显示,可对表达式或变量求值,并将结果显示在其被包含的HTML标签内,替换原有HTML文本。这里需要与th:utext:区分开,th:text:例子如下:
若
restraunt.welcome=welcome to our <b>delicious</b>restaurant!那么,用
<p h:text="#{restaurantt.welcome}"></p> 解析的结果为: welcome to our <b>delicious</b>restaurant! ,也就是说,会输出
welcome to our <b>delicious</b>restaurant</>当然,我们是不会希望页面上出现<和e>的,这时候,我们就需要使用th:utext:来进行转义,即用
<p h:utext="#{restaurant.welcome}"></p>所以最终输出的结果为:welcome to our delicious restaurant!
3.th:object:
用于表单数据对象绑定,将表单绑定到后台controller的一个JavaBean参数,常与th:field一起使用进行表单数据绑定。选择表达式一般跟在th:object后,直接取object中的属性。 这里有一个需要注意的点:*{...}表达式的值是在选定的对象而不是整个context的map。也就是说,如果没有选定的对象,*{...}和${...}没有区别,请看下面的例子:
- <div th:object="${session.user}">
-
- <p>姓名:<span th:text="*{Name}">noodles</span></p>
-
- <p>年龄:<span th:text="*{age}">24</span></p>
-
- <p>国籍:<span th:text="*{nationlity}">中国</span></p>
-
- </div>
上面这段代码相当于:
- <div>
-
- <p>姓名:<span th:text="${session.user.Name}">noodles</span></p>
-
- <p>年龄:<span th:text="${session.user.age}">24</span></p>
-
- <p>国籍:<span th:text="${session.user.nationlity}">中国</span></p></div>
4.th:field:上面提到了一个新标签,th:field:,常用于表单字段绑定。通常与th:object一起使用。 属性绑定、集合绑定。
- <form th:action="@{/bb}" th:object="${user}" method="post" th:method="post">
-
- <input type="text" th:field="*{name}"/>
-
- <input type="text" th:field="*{msg}"/>
-
- <input type="submit"/>
-
- </form>
5.th:action:定义后台控制器路径,类似<form>标签的action属性。
<form action="subscribe.html" th:action="@{/subscribe}">6.th:href:定义超链接,类似<a>标签的href 属性。value形式为@{/logout}.
- <!-- 输出: 'http://localhost:8080/gtvg/order/details?orderId=3' -->
-
- <a href="details.html"
-
- th:href="@{http://localhost:8080/gtvg/order/details(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a>
-
- <!-- 输出: '/gtvg/order/details?orderId=3' -->
-
- <a href="details.html" th:href="@{/order/details(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a>
-
- <!-- 输出: '/gtvg/order/3/details' -->
-
- <a href="details.html" th:href="@{/order/{orderId}/details(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a>
7.th:src:用于外部资源引入,类似于<script>标签的src属性,常与@{}一起使用。
<script th:src="@{/js/jquery/jquery-2.4.min.js}">8.th:value:用于标签赋值,类似<option>标签的value属性。
- <option th:value="soup">soup</option>
-
- <input id="msg" th:value="${msg}" />
9.th:if or th:unless:条件判断,支持布尔值,数字(非零为true),字符,字符串等.
- <div th:if="${restaurant.index} == 0">... I love eating(do something at here) ...</div>
-
- <span th:if="${food.price lt 100}" class="offer">Special desert!</span> /*不能用"<",">"等符号,要用"lt"等替代*/
-
- <select class='form-control' name="skill[4].proficiency">
-
- <option >掌握程度</option>
-
- <option th:if="${skill.level eq '一般'}" th:selected="selected">一般</option>
-
- <option th:if="${skill.level eq '熟练'}" th:selected="selected">熟练</option>
-
- <option th:if="${skill.level eq '精通'}" th:selected="selected">精通</option>
-
- </select>
这里有两个需要注意的点:先看下面两行代码,
- <div th:if="${user.isAdmin()} == false"> ...
-
- <div th:if="${user.isAdmin() == false}"> ...
在这个例子中,==false是写在了...的外边,所以使Thymeleaf本身在支持它,如果写在了
{...}的里边,则变为由OGNL或SpringEL库来支持它。(***这里目前我还未明白是什么意思,希望明白的大神能告诉我这个问题***)
而null值也可以这么使用:
<div th:if="${variable.something} == null"> ... th:if不光可以使用布尔值,以下规则都可以:
- 如果值不为空:如果值为null,th:if将为false
- 如果值为布尔型并且为true
- 如果值为数值型并且不为0
- 如果值为character并且不为0
- 如果值为String,并且不为"false","off"和"no"
- 如果值不为布尔型,数值型,character或String的任意类型
● 如果值为null,th:if将为false
th:if还有一个互逆的表达式为th:unless,还继续用之前的例子作一个演示:
- <a href="comments.html"
-
- th:href="@{/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}"
-
- th:unless="${#lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}">查看</a>
下面的是一个th:if 例子,大家可以照着套一下。
- <table>
-
- <tr>
-
- <th>食物名称</th>
-
- <th>食物价格</th>
-
- <th>可现做</th>
-
- <th>食客评价</th>
-
- </tr>
-
- <tr th:each="prod:${prods}">
-
- <td th:text="${prod.name}">醋溜土豆丝</td>
-
- <td th:text="${#numbers.formatDecimal(prod.price,0,2)}">2.41</td>
-
- <td th:text="${prod.isReady}?#{true}:#{false}">yes</td>
-
- <td>
-
- <span th:text=${#lists.size(prod.comments)}>2</span>个评价
-
- <a href="comments.html" th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}"
-
- th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}">查看</a>
-
- </td>
-
- </tr>
-
- </table>
如果产品有评论,那么我们就创建一个跳转到评论页面的超链接,并且使用产品ID作为参数。
10.th:switch 和th:case:选择语句。 th:case="*"表示default case。注意:一旦一个th:case被判断为真,那么其他的同等级的th:case都将被判断为假
- <div th:switch="${user.role}">
-
- <p th:case="'admin'">超级管理员用户</p>
-
- <p th:case="#{roles.manager}">管理员用户</p>
-
- <p th:case="*">其他用户</p>
-
- </div>
11.th:with:定义变量,th:with="isEven=${prodStat.count}%2 == 0",定义多个变量可以用逗号分隔。
- <div th:with="firstPer=${persons[0]}">
-
- <p>
-
- The name of the first person is <span th:text="${firstPer.name}">Julius Caesar</span>.
-
- </p>
-
- </div>
当th:with被处理,firstPer变量创建一个局部变量和变量添加到map自上下文,以便它是用于评估和其他上下文中声明的变量从开始,但只有包含< div >标记的范围内。
- div th:with="firstPer=${persons[0]},secondPer=${persons[1]}">
-
- <p>
-
- The name of the first person is <span th:text="${firstPer.name}">Julius Caesar</span>.
-
- </p>
-
- <p>
-
- But the name of the second person is
-
- <span th:text="${secondPer.name}">Marcus Antonius</span>.
-
- </p>
-
- </div>
th:with属性允许重用变量定义在相同的属性:
<div th:with="company=${user.company + ' Co.'},account=${accounts[company]}">...</div>12.th:remove:移除除了第一个外的静态数据,用第一个tr标签进行循环迭代显示:
- <tbody th:remove="all-but-first">
-
- //将后台传出的 productList 的集合进行迭代,用product参数接收,通过product访问属性值
-
- <tr th:each="product:${productList}">
-
- //用count进行统计,有顺序的显示
-
- <td th:text="${productStat.count}">1</td>
-
- <td th:text="${product.description}">Red Chair</td>
-
- <td th:text="${'$' + #numbers.formatDecimal(product.price, 1, 2)}">$123</td>
-
- <td th:text="${#dates.format(product.availableFrom, 'yyyy-MM-dd')}">2014-12-01</td>
-
- </tr>
-
- <tr>
-
- <td>White table</td>
-
- <td>$200</td>
-
- <td>15-Jul-2013</td>
-
- </tr>
-
- <tr>
-
- <td>Reb table</td>
-
- <td>$200</td>
-
- <td>15-Jul-2013</td>
-
- </tr>
-
- <tr>
-
- <td>Blue table</td>
-
- <td>$200</td>
-
- <td>15-Jul-2013</td>
-
- </tr>
-
- </tbody>
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/FurtherSkyQ/article/details/117782790
所属网站分类: 技术文章 > 博客
作者:天使之恋
链接:http://www.javaheidong.com/blog/article/221922/041e97f5ec5fcf122ba8/
来源:java黑洞网
任何形式的转载都请注明出处,如有侵权 一经发现 必将追究其法律责任
昵称:
评论内容:(最多支持255个字符)
---无人问津也好,技不如人也罢,你都要试着安静下来,去做自己该做的事,而不是让内心的烦躁、焦虑,坏掉你本来就不多的热情和定力